Understanding Bonds and Investment Opportunities
May 17, 2024 By Triston Martin
Bonds, as a crucial part of the financial world, give people who invest a way to distribute money and gain earnings. They are like steady income securities that show loans given by investors usually to governments or companies. For those investors who want to spread their investments and handle risk well, knowing about bonds is very important. In this detailed guide, we will delve into the world of bonds, how they work, their types, and methods to invest smartly in them.
An Overview of Bonds
Bonds work like debts. They are used by those who need money (issuers) to borrow from people with extra funds (investors). When you buy a bond, it means you are lending money to the issuer of that bond. In return for your loan, they promise to pay regular interest on what has been lent out. This payment is called "coupon payment". Also at the end time when the bond matures or ends its period, the full amount borrowed called the principal will be given back along with any remaining interest left unpaid. The main sum of money that was put in at first by a person holding bonds is known as "Face Value". Varieties of bonds are government bonds, corporate bonds, municipal bonds, and treasury bonds. Every kind has its features and level of risk.
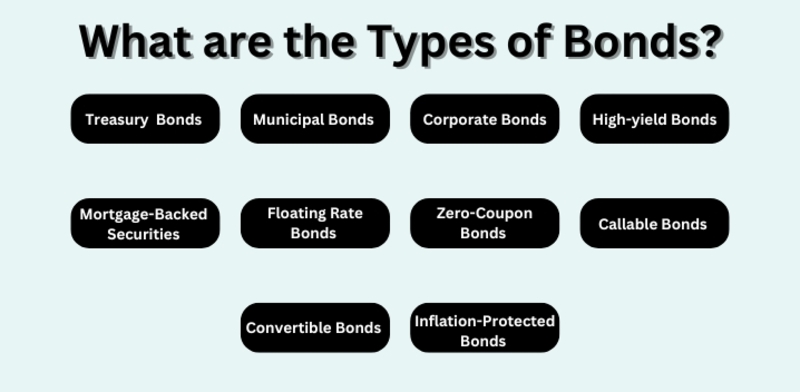
Recognizing bond types is very important for investors who want to spread out their portfolios in a good way. Low-risk government bonds are supported by national governments, and this provides stability for the investors. Corporate bonds have more earnings but also a higher credit risk as they depend on how well the company is doing. Bonds from Municipalities, which are given out by local governments, give tax benefits and help in the growth of communities. Treasury Bonds, supported by the government's complete faith and credit, usually seen as safe-haven possessions attract investors who avoid risks.
- Tax implications: Municipal bonds may offer tax-exempt income, making them attractive for certain investors.
- Market liquidity: Treasury bonds typically exhibit high liquidity, allowing investors to buy and sell with ease.
How Bonds Work?
Bonds work based on a contract between the one who gives out the bond and the person buying it. The issuer, which can be a government or corporation, promises to give back the main amount to the bondholder when a bond reaches its maturity date along with regular interest payment. These interest payments are set by what's called the coupon rate of the bond and they usually happen twice in a year or yearly. Bonds quickly change their prices according to variations in interest rates, the strength of credit from issuers, and how much people want them. Investors need to comprehend these movements so they can make intelligent choices about their bond investments.
Furthermore, bonds can be used as a tool for managing risk in investment portfolios. Bonds have stable income characteristics which assist in balancing the overall risk of a portfolio, especially during uncertain economic situations. They also provide diversification benefits by reducing correlation with equities and improving returns adjusted to risk for investors.
- Inflation protection: Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities (TIPS) adjust their principal value based on changes in the Consumer Price Index, offering protection against inflation.
- Duration risk: Longer-term bonds are more sensitive to changes in interest rates, posing higher duration risk to investors.
Types of Bonds
Diverse bond types cater to varying investor preferences and risk appetites. Government bonds, issued by national governments, are renowned for their low default risk and are often considered safe-haven assets. Corporate bonds, on the other hand, are issued by corporations to raise capital for business operations or expansion projects. These bonds offer higher yields than government bonds but entail greater credit risk. Municipal bonds are issued by state or local governments to finance public projects and infrastructure development, while treasury bonds are issued by the government to finance budget deficits and governmental expenditures.
Investors must assess the risk-return profile of each bond type before making investment decisions. Government bonds, backed by sovereign entities, provide relative safety but lower yields compared to corporate bonds. Corporate bonds offer higher income potential but carry credit risk associated with the issuing corporation's financial health. Municipal bonds combine tax advantages with moderate risk, appealing to investors in higher tax brackets seeking income with reduced tax liabilities.
- Credit risk assessment: Investors should evaluate the creditworthiness of bond issuers by examining credit ratings provided by rating agencies.
- Callable bonds: Some bonds allow issuers to redeem them before maturity, presenting reinvestment risk to bondholders.
Factors to Consider When Investing in Bonds
When investors include bonds in their investment collections, they must think about many things. This involves the credit rating of the bond, which shows how much trust investors have in its issuer and the chances of not paying back money owed, the date when it will mature and yield to maturity (YTM). Other elements that can affect bond prices and yields are current market interest rates along with predictions for inflation. Diversification across bond types and maturities can mitigate risk and enhance portfolio stability.
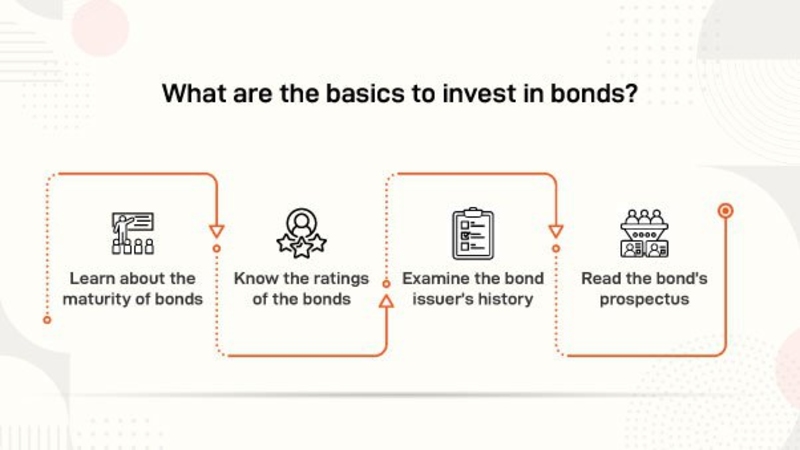
Additionally, people who invest money need to evaluate how much risk they can handle and what they want from their investments when picking bonds for their collection. Those who are more careful might focus on keeping the money safe and having a regular income, so they could prefer high-quality bonds that come with less credit risk. On the other hand, those investors who are more aggressive may look for bigger returns by gaining access to riskier bond types like high-yield or bonds from developing markets.
- Liquidity considerations: Investors should ensure that bonds selected for their portfolios offer sufficient liquidity for buying and selling.
- Reinvestment risk: Falling interest rates may lead to lower coupon payments upon reinvestment, affecting overall portfolio returns.
Strategies for Bond Investing
There are different plans for investing in bonds, based on the goals and risk acceptance of each investor. One strategy is to buy and keep, which means buying bonds to hold them until they mature so you can get coupon payments and also receive the principal amount. On the other hand, there is active bond management that includes frequent trade of bonds to take advantage of market inconsistencies and changes in interest rates. A well-liked method is bond laddering, where you buy bonds that will become due at different times to balance danger and keep cash ready.
Furthermore, bond mutual funds or exchange-traded funds (ETFs) are also an option for investors. These tools allow people to access diverse bond portfolios that have been professionally managed by fund managers. Such funds provide ease of use and spreading of risk benefits, making them appropriate for investors who desire wide market coverage without having to pick and handle each bond individually.
- Yield curve positioning: Investors may adjust the duration of their bond portfolios based on their outlook on interest rates and the shape of the yield curve.
- Tax-efficient investing: Municipal bond funds can provide tax advantages for investors in higher tax brackets, enhancing after-tax returns.
Conclusion
Bonds have a significant part in investment collections, providing balance, earnings, and distribution advantages. By comprehending how bonds operate and the different investing possibilities they offer, investors can make knowledgeable choices to reach their monetary objectives. The world of bonds is wide-ranging and diverse, offering a range of options that suit many investor preferences. For those who seek consistent income sources or safeguard their capital value over time - bonds are an important asset class to consider as you plan your journey towards building wealth.

The Gamma Squeeze: What Is It?

Buy or Sell Stocks

Unlocking the Power of ISO 20022: AI-Driven Insights for Financial Institutions
Bear Flag Pattern: A Step-by-Step Guide for Navigating Bearish Markets
Understanding the Differences Between Futures and Forwards Contracts

A Beginners Guide to Ordinary Shares - Its Benefits and More

Understanding Bonds and Investment Opportunities

Methods to Efficiently Cash Out Your Life Insurance Policy

ETF vs. Index Fund: An Overview

